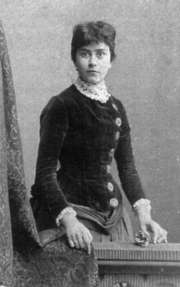|
Biography Else Lasker- Schuler
born Feb. 11, 1869, Elberfeld, Ger.
died Jan. 22, 1945, Jerusalem, Palestine
Else Lasker-Schüler (February 11, 1869 – January 22, 1945) was a Jewish German poet and playwright (1869-1945) famous for her bohemian lifestyle in Berlin. She was one of the few women affiliated with the Expressionist movement. Lasker-Schüler fled Nazi Germany and lived out the rest of her life in Jerusalem
Schüler was born in Elberfeld, now a district of Wuppertal. Her mother, Jeannette Schüler (née Kissing) was a central figure in her poetry, and the main character of her play Die Wupper was inspired by her father, Aaron Schüler, a Jewish banker.
In 1894, Else married the physician and occasional chess player, Jonathan Berthold Lasker (the older brother of Emanuel Lasker, a World Chess Champion) and moved with him to Berlin, where she trained as an artist. On August 24, 1899 her son Paul was born and her first poems were published. She published her first full volume of poetry, Styx, three years later, in 1902. On April 11, 1903, she and Berthold Lasker divorced and on November 30, she married Georg Lewin. His pseudonym, Herwarth Walden, was her invention.
Lasker-Schüler's first prose work, Das Peter-Hille-Buch, was published in 1906, after the death of Hille, one of her closest friends. In 1907, she published the prose collection Die Nächte der Tino von Bagdad, followed by the play "Die Wupper" in 1909, which was not performed until later. A volume of poetry called the Meine Wunder, published in 1911, established Lasker-Schüler as the leading female representative of German expressionism.
After separating from Herwarth Walden in 1910 and divorcing him in 1912, she found herself penniless and dependent on the financial support of her friends, in particular Karl Kraus. That year, she met Gottfried Benn. An intense friendship developed between them which found its literary outlet in a large number of love poems dedicated to him. The death of her son in 1927, however, sent her into a deep depression.
Despite winning the Kleist Prize in 1932, as a Jew she was physically harassed and threatened by the Nazis. She emigrated to Zürich but there, too, she could not work. She traveled to Palestine in 1934 and finally settled in Jerusalem in 1937. In 1938 she was stripped of her German citizenship and the outbreak of World War II prevented any return to Europe.
In 1944 Lasker-Schüler's health deteriorated. She suffered a heart attack on January 16, and died in Jerusalem on January 22, 1945. She was buried on the Mount of Oliv
Works
Lasker-Schüler left behind several volumes of poetry and three plays, as well as many short stories, essays and letters. During her lifetime, her poems were published in various magazines, among them the journal Der Sturm edited by her second husband, and Karl Kraus' 'Fackel. She also published many anthologies of poetry, some of which she illustrated herself. Examples are:
Styx (first published volume of poetry, 1902)
Der siebente Tag (second volume of poetry, 1905)
Meine Wunder (first edition, 1911)
Gesammelte Gedichte (1917)
Mein blaues Klavier (1943)
Lasker-Schüler wrote her first and most important play, Die Wupper, in 1908. It was published in 1909 and the first performance took place on April 27, 1919 at the Deutsche Theater in Berlin.
A large part of her work is composed of love poetry, but there are also deeply religious poems and prayers. Transitions between the two are often quite fluid. Her later work is particularly rich in biblical and oriental motifs. Lasker-Schüler was very free with regard to the external rules of poetic form, however her works thereby achieve a greater inner concentration. She was also not averse to linguistic neologisms.
A good example of her poetic art is "Ein alter Tibetteppich" ("An old Tibetan rug"), a poem which was reprinted many times after its first publication in Sturm, the first of these being in Fackel.
|